

24/10/2016
Ciliopathies are a group of diseases characterized by impaired functioning of the cilium, an organelle located on the cell surface. These diseases affect many organs and tissues, such as the kidney, retina, and heart.
Although pancreatic cells are ciliated, no pancreatic disease has yet been clearly linked to a ciliary defect. Using transgenic mice, Patrick Jacquemin and his co-workers found a tight correlation between defective cilia in pancreatic cells and progressive development of chronic pancreatic inflammation, which is known to predispose to pancreatic cancer. These observations can account for the increased risk to develop pancreatic cancer in patients with a Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, a genetic disease associated with development of gastro-intestinal tumors.
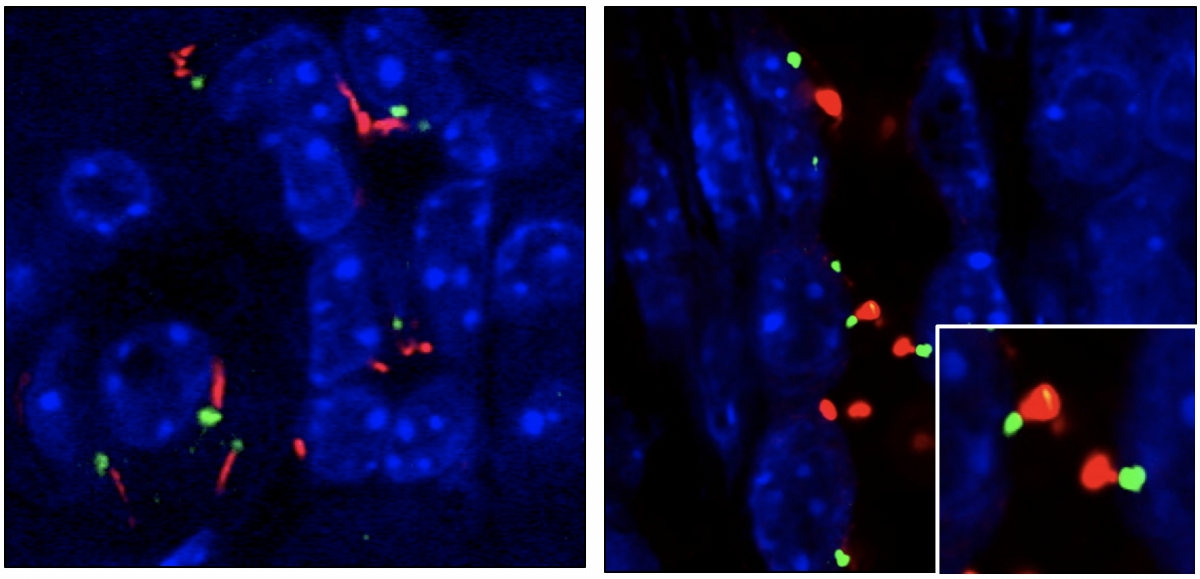
Primary cilia of normal (left) and transgenic (right) mice. Cilia in transgenic mice are shorter and have a swollen tip.
Article describing this research
Augereau C, Collet L, Vargiu P, Guerra C, Ortega S, Lemaigre FP, Jacquemin P.
Human Molecular Genetics. (2016), 25(22):5017-26